In the digital age, your smartphone holds everything—photos, messages, banking, health data, and private communications. That’s why security is critical when choosing between an iPhone or Android phone.
While both platforms offer high-tech features, Apple’s iPhone consistently ranks as the more secure option. Let’s explore exactly why that is—and, for Android fans, how you can still lock down your device effectively.
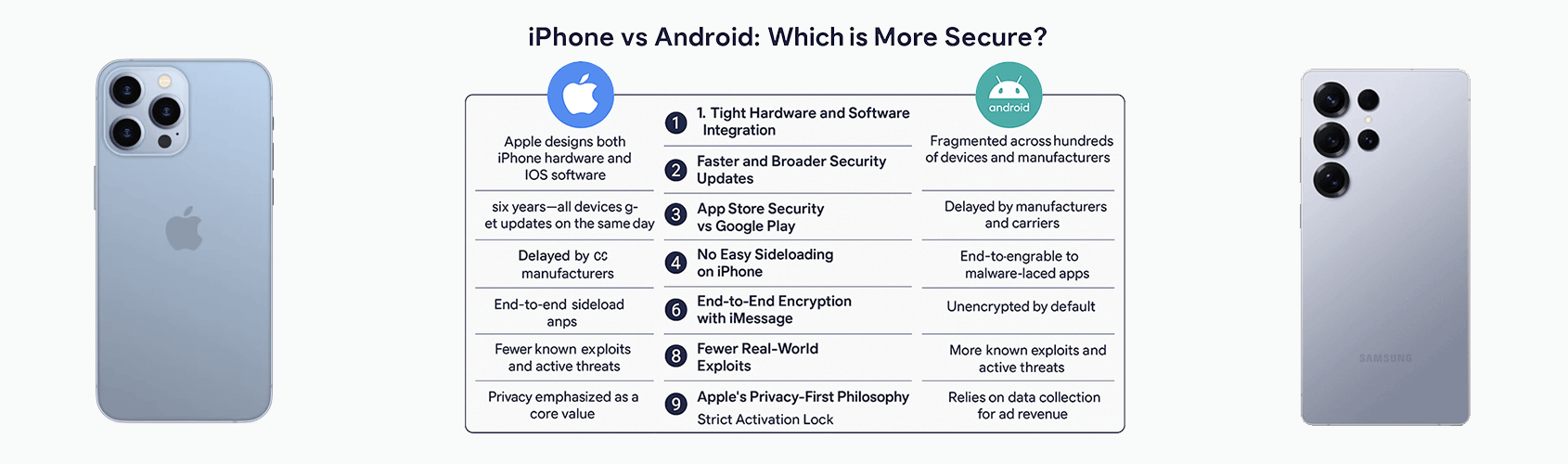
1. Tight Hardware and Software Integration
Apple designs both the iPhone hardware and the iOS software, resulting in a tightly integrated ecosystem. This lets Apple control security at every level—something Android simply can’t match due to its fragmented nature across hundreds of devices and manufacturers.
2. Faster and Broader Security Updates
Apple supports older iPhones with software updates for up to six years—and all devices get updates on the same day.
Android updates are delayed by manufacturers and carriers, and many Android devices stop receiving updates after just 2–3 years. This delay leaves millions of users exposed to unpatched security vulnerabilities.
3. App Store Security vs Google Play
Apple’s App Store has strict review policies, manual app inspections, and advanced malware scanning. As a result, it’s rare to see malicious apps make it through.
The Google Play Store has improved, but historically has been more vulnerable to malware-laced apps—especially when users download from third-party app stores, a much easier process on Android.
4. No Easy Sideloading on iPhone
One of iOS’s biggest advantages? It’s hard to sideload apps from unknown sources unless a user jailbreaks the phone.
On Android, sideloading is easy with a few taps in the settings menu. While convenient for developers or power users, it greatly increases the risk of installing malicious apps.
5. Secure Enclave: Hardware-Level Security
Each iPhone contains a Secure Enclave, a dedicated chip that handles Face ID, Touch ID, Apple Pay, and encryption keys. This security module is physically isolated from the rest of the system, making it almost impossible to hack.
Some Android phones feature similar tech (like Samsung Knox), but it’s not consistent across all devices.
6. End-to-End Encryption with iMessage
Apple’s iMessage and FaceTime are end-to-end encrypted by default, meaning nobody—not even Apple—can read your messages.
Android’s default messaging system (SMS/MMS) is unencrypted unless users enable Google Messages with RCS, and even then, encryption depends on the recipient’s device.
7. Fewer Real-World Exploits
Security research and vulnerability databases regularly show that Android has more known exploits and active threats than iOS. Whether through malware, spyware like Pegasus, or phishing apps, Android is more frequently targeted.
8. Apple’s Privacy-First Philosophy
Apple emphasizes privacy as a core value, offering features like:
- App Tracking Transparency
- Mail Privacy Protection
- Intelligent Tracking Prevention in Safari
- Lockdown Mode for at-risk users (journalists, diplomats, etc.)
While Google has taken steps to improve Android privacy, its business model still heavily relies on data collection for ad revenue.
9. iPhone Anti-Theft Tools
Apple’s Find My iPhone feature and Activation Lock make it nearly impossible for a thief to reuse a stolen device.
Android’s Find My Device works well, but Activation Lock is less strict and varies by manufacturer, making stolen Android phones more easily reset and resold.
10. Enterprise-Ready from the Start
Apple has earned the trust of governments and corporations due to features like:
- Built-in encryption
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) support
- Remote wipe
- Per-app VPN
Android can do this too, but it depends on the manufacturer and whether the device is part of the Android Enterprise Recommended program.
Banking and Crypto Wallet Security: iPhone vs Android
When it comes to managing your finances on a smartphone, security isn’t just important—it’s everything. Whether you're using mobile banking apps or managing digital assets through crypto wallets like MetaMask or Coinbase, your phone’s security architecture plays a critical role.
iPhone: Built for Financial Confidence
- Secure Enclave encrypts and protects biometric data and cryptographic keys.
- Face ID and Touch ID add hardware-based biometric security to sensitive apps.
- iOS apps run in strict sandboxes, preventing data leaks between apps.
- Apple’s curated App Store reduces the chance of downloading fake or malicious financial apps.
Popular crypto wallets offer full support for iOS security tools, making it a strong choice for managing crypto on the go.
Android: Secure When Properly Configured
- Top-tier Android devices like Pixel and Samsung support hardware-backed key storage with TEE or StrongBox.
- Users must avoid sideloading or unverified apps to prevent exposure.
- Fragmented device support means not all Android phones offer the same level of protection.
In short, iPhones offer better out-of-the-box financial security, while Android requires device selection and careful configuration to meet the same standard.
Still Prefer Android? Here’s How to Secure Your Android Phone
If you love Android's flexibility, don't worry—you can still enjoy your device while tightening your security. Here’s how:
🔒 1. Keep It Updated
Always install the latest system and Play Store security updates. If your phone no longer receives updates, consider switching to a Pixel device for better long-term support.
🛡️ 2. Avoid Sideloading
Don't install apps from unknown sources. Turn off the "Install unknown apps" option unless absolutely necessary.
✅ 3. Use Google Play Protect
Make sure Play Protect is enabled under the Google Play Store settings to scan apps regularly.
🪜 4. Clean Out Unused Apps
Delete apps you don’t use. Each app is a potential entry point for data collection or exploitation.
🔐 5. Strengthen Your Lock Screen
Use biometrics (fingerprint or face unlock) along with a strong PIN or password. Avoid swipe or pattern unlocks.
🧩 6. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Set up 2FA for your Google Account and any sensitive apps like banking, email, or cloud storage.
🛡️ 7. Consider a Trusted Security App
Security apps like Bitdefender, Malwarebytes, or Norton can add extra protection from threats.
📱 8. Use Secure Messaging
Use encrypted messaging apps like Signal, Telegram, or WhatsApp to protect your communications.
🌐 9. Use a VPN
When using public Wi-Fi, a VPN can help encrypt your traffic and reduce exposure to attackers.
👤 10. Audit App Permissions
Go to Settings > Privacy and review each app's access. Deny anything unnecessary (like camera or microphone access for a calculator app).
Final Thoughts
If you’re serious about mobile security, the iPhone is the clear winner. Apple’s tight ecosystem, frequent updates, strict app controls, and privacy-focused approach set the gold standard.
But if you still prefer Android’s flexibility and customization, you can absolutely make it more secure—you just need to be proactive and vigilant.
And whether you’re checking your bank balance or managing crypto, the phone you use should never be the weak link in your digital security.